Last updated August 01, 2019
Channels lets you push events to clients over a WebSocket via a simple API call. To install Channels as a Heroku add-on, simply follow the steps below.
Let’s say you want to add Channels an existing Rails 3 app. We’ll assume you’ve already created your app on Heroku.
Install Channels Gem
Start by installing the Channels gem, or adding it to your Gemfile.
$ gem install pusher
Install add-on
$ heroku addons:create pusher:sandbox
Configure for local use
Get your ‘development’ Channels credentials for your local app:
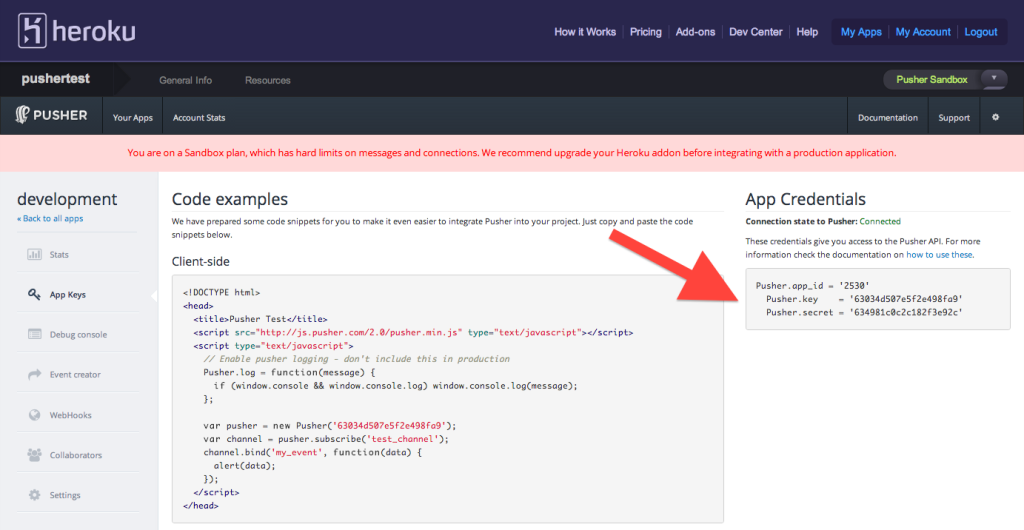
Configure your app for development mode only. In Rails, this would go in config/environments/development.rb:
require 'pusher'
Pusher.app_id = 'YOUR_CHANNELS_APP_ID'
Pusher.key = 'YOUR_CHANNELS_KEY'
Pusher.secret = 'YOUR_CHANNELS_SECRET'
Production credentials
Channels will automatically be configured to use your ‘heroku’ application when you deploy it as long as the gem is in your Gemfile:
gem 'pusher'
Verifying your set up
Set up a view
In one of your templates, you will now need to configure a Channels connection for your Javascript. The following subscribes to a channel called ‘test_channel’ and listens for the ‘greet’ event:
<script src="//js.pusher.com/4.4/pusher.min.js"></script>
<script>
// If your Heroku application is within the EU region,
// uncomment the followling lines
// Pusher.host = 'ws-eu.pusher.com';
// Pusher.sockjs_host = 'sockjs-eu.pusher.com';
var pusher = new Pusher('<%= Pusher.key %>'); // uses your APP KEY
var channel = pusher.subscribe('test_channel');
channel.bind('greet', function(data) {
alert(data.greeting);
});
</script>
Triggering events
In your Rails controllers, you now can trigger events that your connected clients will receive. This is relatively simple:
Pusher['test_channel'].trigger('greet', {
:greeting => "Hello there!"
})
Now every time you push to Heroku your app will be automatically configured to use the “heroku” app created in your Pusher Channels panel.
Going further
Hopefully this has given you a taste of the great stuff you can do with Channels. We recommend having a look through our Channels documentation to get an idea of what else is available.
In particular, the section on Debugging is particularly useful. Remember that you have access to your Channels dashboard from within Heroku’s panel.