Table of Contents [expand]
Last updated February 05, 2026
Heroku integrates with GitHub to make it easy to deploy code living on GitHub to apps running on Heroku. When GitHub integration is configured for a Heroku app, Heroku can automatically build and release (if the build is successful) pushes to the specified GitHub repo.
Enabling GitHub Integration
You can configure GitHub integration in the Deploy tab of apps in the Heroku Dashboard.
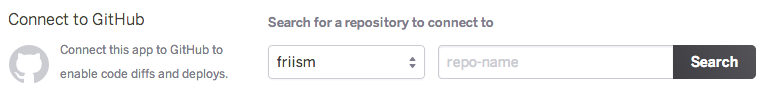
To configure GitHub integration, you have to authenticate with GitHub. You only have to do this once per Heroku account.
GitHub repo admin access is required for you to configure automatic GitHub deploys. This is because Heroku has to register a service hook on the GitHub repo, and this action requires admin access. For GitHub organisations, your GitHub account will also need to be a member of the organisation and not an outside collaborator.
If your repo is in a GitHub organization that has third-party application restrictions enabled, an organization admin needs to approve Heroku for use with the organization. More details are available on GitHub.
After you link your Heroku app to a GitHub repo, you can selectively deploy from branches or configure auto-deploys.
If you do not have any apps, you must approve integration for your organization from GitHub. For more information about this process, see Approving OAuth Apps for your organization.
Manual Deploys
With manual deploys, you can create an immediate deployment of any branch from the GitHub repo that’s connected to your app. Use manual deploys if you want to control when changes are deployed to Heroku.
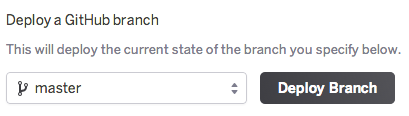
You can also use manual deploys to temporarily deploy a branch other than the one that’s configured for automatic deployment. For example, you might have a development app synced to the development GitHub branch, but you temporarily want to test a feature branch. Simply trigger a manual deploy of the feature branch to test it on the Heroku app. Note that release of the feature branch is overwritten on the next successful GitHub push to the development branch.
Automatic Deploys
When you enable automatic deploys for a GitHub branch, Heroku builds and deploys all pushes to that branch. If, for example, you have a development app on Heroku, you can configure pushes to your GitHub development branch to be automatically built and deployed to that app.
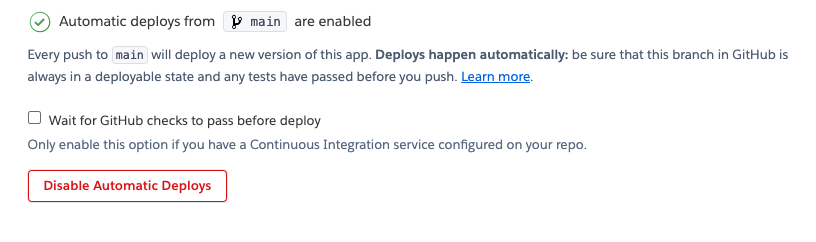
If you’ve configured your GitHub repo to use automated Continuous Integration (with Travis CI, for example), you can check the “Wait for CI to pass before deploy” checkbox. When enabled, Heroku will only auto-deploy after all the commit statuses of the relevant commit show success.
This commit won’t auto-deploy because one of the checks shows a pending status:
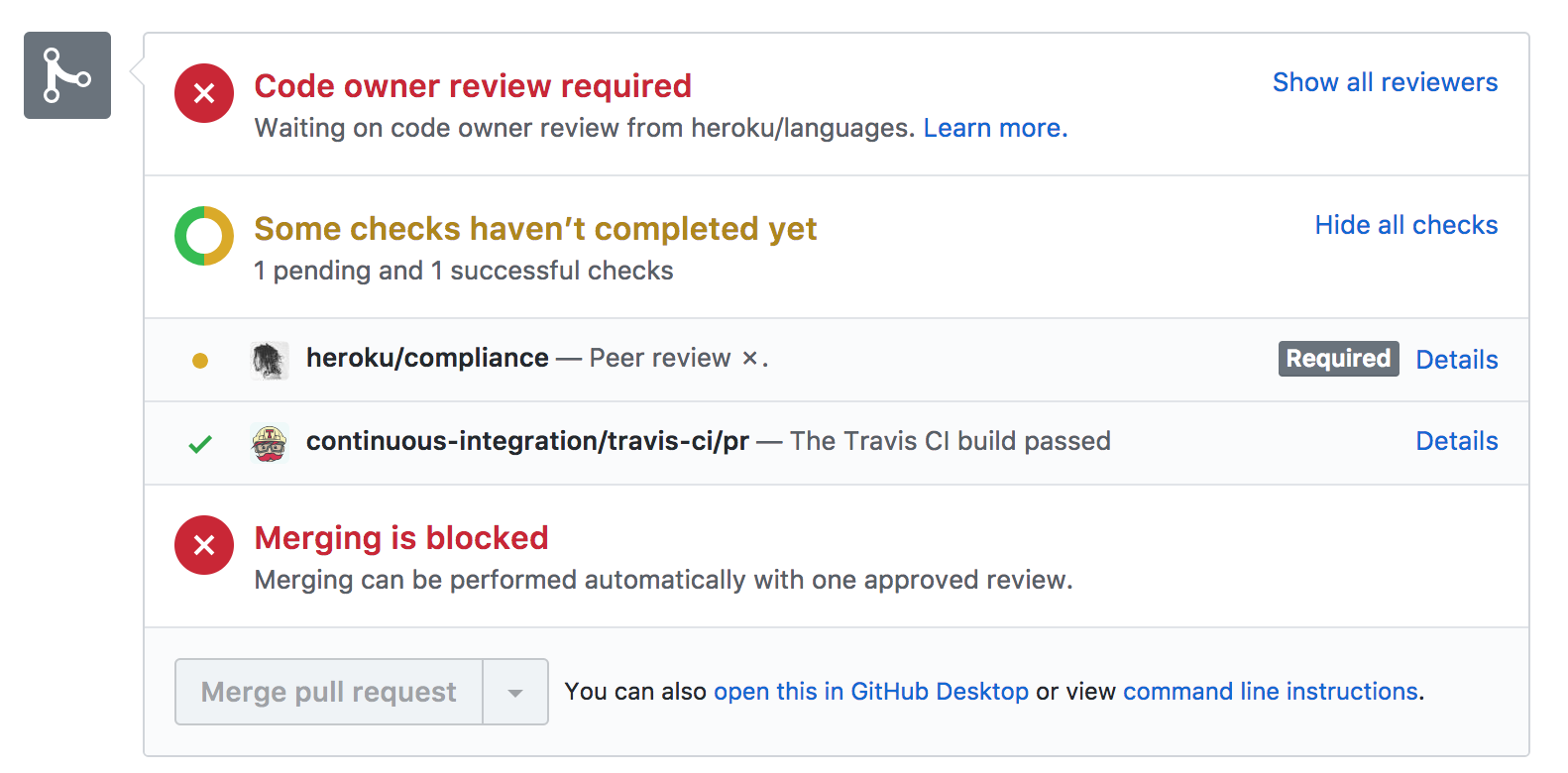
This commit will auto-deploy because all of the checks show a status of success:
Review Apps
With review apps enabled for a Heroku app, Heroku will create temporary test apps for each pull request that’s opened on the GitHub repo that’s connected to the parent app. Review apps are great if you’re using GitHub Flow to propose, discuss, and merge changes to your code base. Because pull request branches are deployed to new apps on Heroku, it’s very simple for you and your collaborators to test and debug code branches. You can also run automated integration tests on the Heroku app representing a GitHub branch.
See the Review apps article for details.
Heroku CI
Once you’ve connected your GitHub repo to your Pipeline, you can turn on Heroku CI, our visual, low-configuration test runner that integrates easily with Heroku Pipelines (and so complements Review apps, existing Heroku apps, and our GitHub integrations). Any Heroku Pipeline is already Heroku CI ready – just turn it on in the Pipeline’s Settings tab.
Links to Diffs
For apps that are linked to GitHub repos, releases in the Dashboard Activity tab will include a “View Diff” link. Following the link will take you to the GitHub comparison view, showing the changes made since the last release.

Disconnecting from GitHub
Disconnecting Individual Apps
Individual apps can be disconnected in the GitHub pane of the Deploy tab for the app.

Disconnecting Account
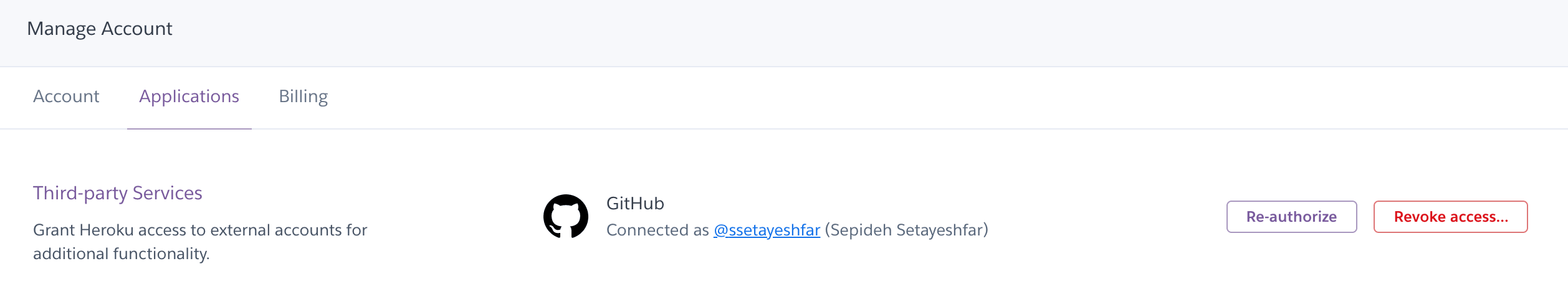
You can disconnect your Heroku and GitHub accounts in the Applications pane on your Dashboard account page.
FAQ
Does the GitHub integration sync to my Heroku-hosted Git repo?
For apps with GitHub integration enabled, Heroku does not sync the contents of the GitHub repo to the Heroku-hosted repo. Instead, Heroku pulls source directly from GitHub. Although you can technically still push code to your Heroku Git remote, you should refrain from doing so, because it might confuse collaborators as to what code is currently deployed to the app.
What if I use a version control provider besides GitHub?
Heroku does not currently provide a first-party deployment integration for version control providers besides GitHub. Please see this article for deployment options if you use another version control provider, such as GitLab or Bitbucket.
Where can I view build output?
Build output is available in the application’s Activity tab on Heroku Dashboard. You can view historical build output and also stream output of builds in progress.
Does GitHub integration automatically run schema migrations?
By default, Heroku does not run migrations specified by frameworks like Rails during deploys.
Heroku Release Phase lets you perform common tasks like schema migrations before a new version of your app is run. See its documentation for more information.
Does GitHub integration work with Git Submodules?
GitHub repos that use submodules will generally not deploy correctly on Heroku. This is because GitHub does not include submodule contents when repo-content tarballs are generated.
Why can’t Heroku access my GitHub repository?
When the GitHub integration is unable to access contents of your repository, it is generally caused by one of the following reasons:
- The GitHub user has lost access to the repository. This can be addressed by requesting access to the repository again, or using a different GitHub user.
- Third-party application restrictions have been enabled on the organization. When third-party application restrictions are enabled, the
Heroku DashboardOAuth application has to be granted access to the organization. For instructions on how to do so, please refer to the GitHub documentation. - The repository no longer exists.
- The GitHub user is an outside collaborator on an organisation, which isn’t currently supported. The user needs to be a member of the organisation.
Why is the wrong user attributed to deploys in the activity log?
When we trigger a build due to a notification from GitHub, we receive the GitHub user ID, we try and find a linked Heroku Account, if we can’t find a linked account matching the GitHub ID, then the user who connected the Pipeline or App to GitHub will likely be displayed.
If you find that a user is not being correctly attributed, then connecting their account to GitHub through Dashboard will likely resolve this problem.
Why does Heroku need read and write permissions to my GitHub repos?
There are several reasons for this:
When a deploy is made from a Review app, the Heroku GitHub integration publishes an deployment status to indicate that your code has been deployed with a link to this.
When you enable Review apps, the service will ensure you have an
app.jsonfile which is necessary to ensure that we can automatically build a Review app, the file will be automatically generated and committed to your repository.In order to drive automated deploys, the GitHub integration service needs to be able to add a custom hook to your repository so it can receive notifications from GitHub when you push changes to branches and validate that these come from GitHub, this requires administrative access to your repositories.
GitHub Apps allow for finer grained control on repositories, but that has not been integrated into the GitHub integration yet. We cannot commit to a timeline but it’s definitely on our radar. Keep an eye on the Heroku Changelog.
If any of these above do not apply, please open a support ticket.